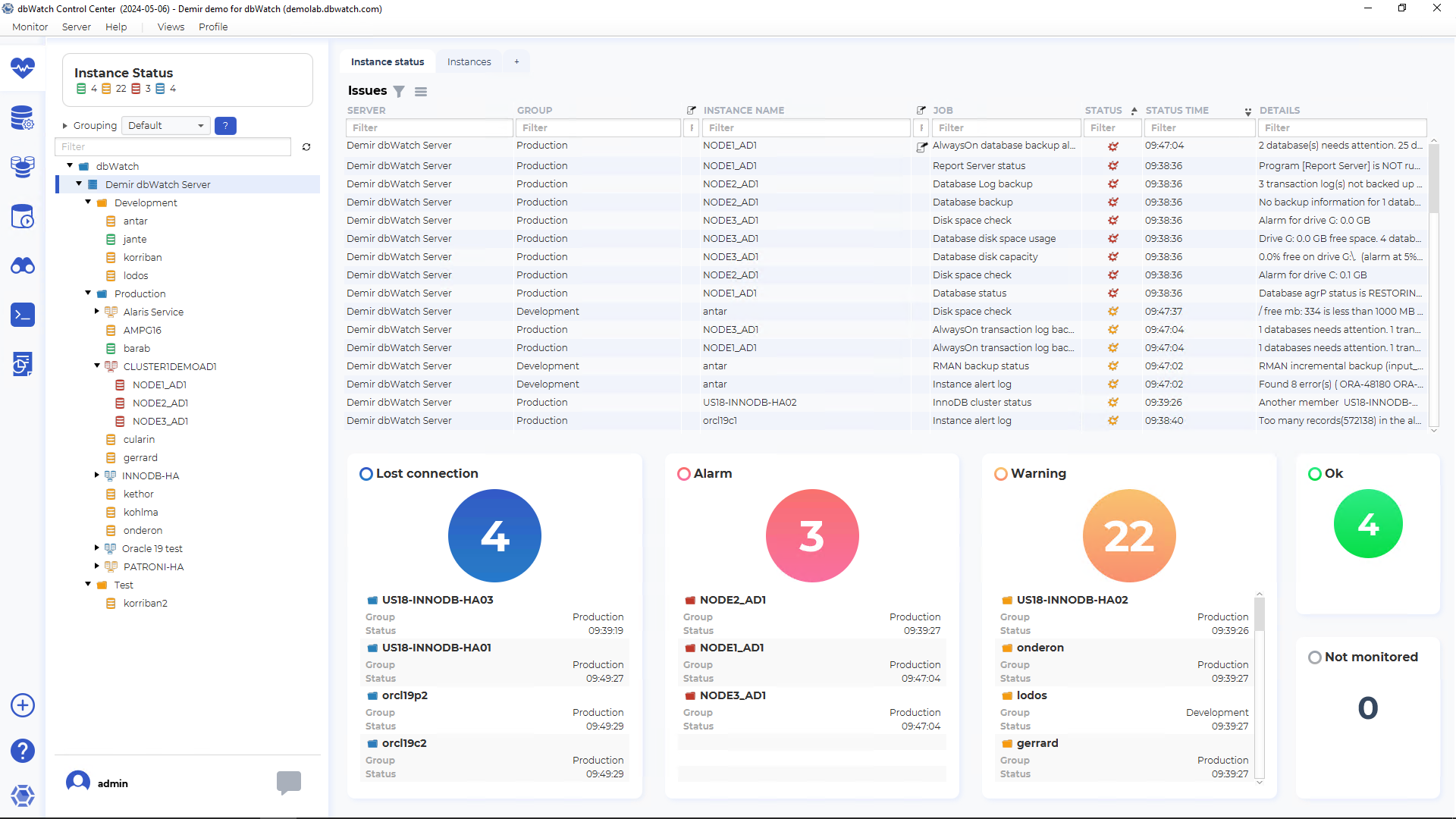
Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) Software tracks and analyzes what’s happening in your databases. It monitors queries, logins, changes, health, security, and database access. A good database activity monitoring tool shows how your databases perform, who is accessing what, and alerts you when something unusual happens.
Because database health and security affect the whole organization, choosing the right database activity monitoring software matters. The tool you select will impact performance, security, compliance, and licensing spend for years to come.
This guide explains what database activity monitoring is, how typical architectures work, and five useful criteria to use when picking a tool.
Before we get to the checklist, it helps to understand how these tools are built and what their architecture looks like.
Database Activity Monitoring Architecture
Beyond features and pricing, you need to consider the tool’s architecture. The architecture determines what the
tool can see, how quickly it reacts, and how much overhead it adds to your databases. Understanding the
architecture helps to avoid misconfiguration, which is one of the most common root causes of security gaps and
missed events.
Most database activity monitoring architectures follow a similar design:
- Data collection layer – collects activity using one or more methods:
- Agent-based: lightweight agents on database servers capturing queries, user sessions, and resource usage.
- Network-based: appliances or virtual sensors that observe database traffic over the network.
- Log-based: parsing transaction logs and native audit logs.
- Analytics and correlation layer – aggregates events, correlates them with policies,
and detects anomalies or suspicious behavior in real time. - Storage and reporting – stores historical activity for forensics, compliance reporting,
and long-term performance analysis. - Alerting and response – sends alerts to database administrators, security teams,
security information and event management / security operations center platforms, and can trigger automated actions
in other tools.
Understanding this architecture helps you compare database activity monitoring tools and decide which approach best
fits your environment (on-premises, cloud, or hybrid).
Once you have this basic picture, you can start evaluating specific database activity monitoring tools against your
own requirements.

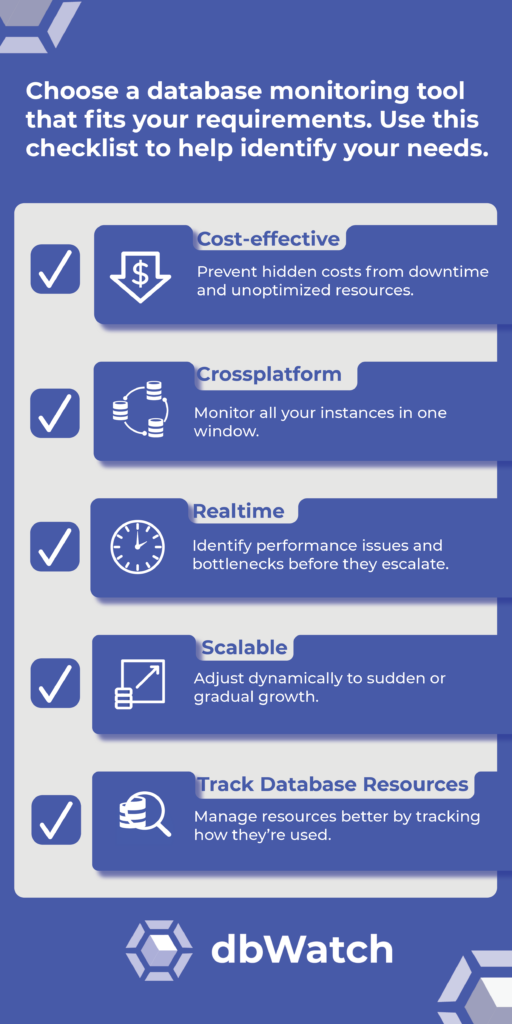
1 Keep Your Database Activity Monitoring Software Cost-effective
As with any purchase your business makes, it’s important to consider the cost. The right database activity monitoring tools reduce IT costs. And they do more than just monitoring; they provide analytics and insights that can lead to significant cost savings. You can optimize resource allocation by finding inefficiencies and bottlenecks, reducing unnecessary spending on hardware upgrades or unneeded added capacity.
Reducing database downtime cuts direct revenue loss and avoids disruptions for customers. Practical monitoring tools mitigate these risks. According to a Gartner study on the impact of downtime, even a short period of downtime can lead to significant financial losses.
2 Find a Database Tool to Manage Cross-platform
Most companies have multiple database platforms. A cross-platform monitoring tool gives you one view and stays compatible as your server setup grows.
In modern IT environments, monitoring also needs strong integrations. The tool should connect with the systems you already use—security, incident management, and application performance monitoring—so teams can correlate issues and resolve them faster. Integrations can also enable automation, such as triggering backups or scaling resources when thresholds are hit.
Scalability is about complexity as much as size. Many organizations run a mix of cloud and on-premises databases, and using separate monitoring tools creates blind spots. Using a cross-platform tool across the whole environment reduces fragmentation and lowers the risk of missing critical issues.
Database Integration Tip
Remember that scalable tools can typically be used to monitor and manage large numbers of servers using various platforms. Before adopting a new tool, check with the developer to make sure that your tool of choice will remain relevant to your business for a long time to come.
3 Choose Scalability to Future-proof Your Database Systems
As organizations grow, your monitoring must scale with it, handling more databases, higher transaction volume etc. A scalable database monitoring tool is vital for accommodating increased loads without compromising performance. It can adjust dynamically, ensuring that sudden spikes in data and gradual increases over time are managed efficiently.
Why You Need Your Tool to Detect New Databases
It’s a typical scenario: A project sets up 30 databases and doesn’t inform IT. The DBA team first hears about them after they crash, and the project lead requests a backup recovery.
Having automated scans spot and integrate new databases into your monitoring systems is a game-changer. This way, you won’t get blindsided. You’ll know about databases right from the start and manage them smoothly.
4 Real-Time Database Activity Monitoring
Real-time database monitoring helps you pinpoint performance issues and bottlenecks before they cause considerable damage. By identifying issues proactively, you maintain database performance and customers aren’t affected. This approach supports service continuity and helps your organization avoid costly downtime and minimize the impact on users and customers.
The benefits include:
- Detect potential failures before they occur
- Provide a continuous audit of data transactions
- Craft a proactive response framework
- Reduce downtime
- Avoid the costly disruption of expected failure
Pick a Tool that Monitors As-is and What Was
While knowing what’s happening as it happens is critical, it’s also helpful when a monitoring tool can analyze past events. Consider this scenario: There’s a ticket complaining that the database was slow at noon. If you don’t know what happened at 12 o’clock, you could try to recreate it, but it’s unlikely. Instead, ensure your database activity monitoring tool includes historical resource usage and the SQL statements performed in that period.
5 Track Your Database Resources
Naturally, you’ll need to track the resource consumption. When you see the big picture of how an instance uses time, memory, and resources, you can quickly know if the instance is working efficiently with enough resources. You can also use that information to match the database with the applications.
To give an analogy: if databases were cars, applications would be drivers. Consider the Mini Cooper. It’s a smart little car, but it won’t win a race, even with the best racing car driver. Conversely, a race car is wasted on a short trip to the corner store. The car type and driver’s skills match to have a system running optimally.
Monitoring information will help define what is needed and ensure you get a Formula 1 Mercedes driven by Max Verstappen when you need to race, and a simpler setup when you only need a Mini Cooper for a ‘milk run.’
Keep Track of the User Pattern
The number of users on the database also gives insight. Choose a tool that tracks long-term user patterns. If something goes wrong, you can see the activity and resource consumption and when the problem happened.
Did it happen at high speed/peak database usage? Or when the “car” was parked? This is also useful when deciding about making changes to your databases. What once was the ‘milk run’ to the store now has many users and needs a ‘bus’ instead of a ‘car’ because the database is much more active.
The user patterns also help with decisions about space. For example, space can be cleared for higher-priority active instances. Or, when an instance’s use is minimal, it can be taken offline or made into a read-only document.
Database monitoring
Putting Database Activity Monitoring Tools in Context
When you step back from the details of the checklist, most database activity monitoring tools and software fall into three broad groups:
- Security-focused database activity monitoring tools – built mainly for security and compliance, with real-time alerting on suspicious access and strong audit reporting.
- Database performance monitoring tools – focused on performance, query tuning, capacity planning, and overall database health, usually used day to day by DBAs.
- Observability platforms with database monitoring – wider observability stacks where database metrics sit alongside application, infrastructure, and log data.
The right choice depends on what problem you are really trying to solve. For regulatory compliance and database security monitoring, a security-focused database activity monitoring tool will make the most sense. Those who need better performance, capacity planning, and visibility across many database platforms, a database performance monitoring tool is usually a better fit. Finally for one place to see applications, infrastructure, and databases together, an observability platform can be the right trade-off.
dbWatch sits in the database performance monitoring category, with some security features – including auditing, access control, and compliance. dbWatch is designed to monitor many databases across platforms, track resource usage and user patterns over time, and help you apply the kind of cost, scalability, real-time, and resource insights described in this checklist to your own environment.
Database Activity Monitoring FAQ
Database activity monitoring touches performance, security, and compliance, and the terminology can overlap with regular database monitoring tools. This short FAQ explains what database activity monitoring is, and what people mean when they talk about database activity monitoring architecture.
What is database activity monitoring (DAM)?
Database activity monitoring (DAM) is the continuous tracking and analysis of database activity such as logins, queries, changes, and access to sensitive data. A database activity monitoring tool collects data in real time, applies rules or analytics to detect suspicious behavior, and provides alerts and audit trails for security and compliance purposes.
What is a database monitoring tool?
A database monitoring tool tracks the health and performance of databases by measuring things like response times, wait events, resource usage, errors, and availability. These tools help database administrators quickly see where bottlenecks and issues are, so they can keep systems fast, stable, and within capacity limits. Some database monitoring tools also include elements of database security monitoring, such as login tracking or anomaly detection.
What is database security monitoring?
Database security monitoring focuses specifically on protecting data from unauthorized access, misuse, or breaches. It includes monitoring database logins, privilege changes, access to sensitive tables or columns, and unusual activity patterns, often integrating with security information and event management (SIEM) systems. Database activity monitoring is one way to implement database security monitoring, alongside other controls such as encryption, access management, and vulnerability management.
What is database activity monitoring architecture?
Database activity monitoring architecture describes how a database activity monitoring solution is built and how it collects, processes, stores, and alerts on database activity. Typical architectures include a data collection layer (agents, network sensors, or log collectors), an analytics layer that correlates events and applies rules, storage for historical data, and alerting and reporting components that integrate with existing tools. Understanding the architecture helps you judge visibility, performance impact, and how well the solution will scale in your environment.








